Blog
All Blog Posts | Next Post | Previous Post

 Add AI superpower to your Delphi & C++Builder apps part 2: function calling
Add AI superpower to your Delphi & C++Builder apps part 2: function calling
Thursday, May 22, 2025

Image generated by Grok
After the AI introduction blog on basic completion, i.e. prompt & answer cycles with the LLM, here is the 2nd part on function calling. This is where things get really interesting for us Delphi & C++Builder developers! We can basically hook up Delphi or C++Builder code to the LLM to let the LLM intelligently execute our code or to give the LLM our data it can then further process.
Integrating Function Calling with Cloud-Based LLMs Using TTMSMCPCloudAI
Large Language Models (LLMs) have become immensely powerful in reasoning, synthesis, and automation tasks. But their capabilities extend far beyond basic conversation—thanks to function calling. This transformative feature allows an LLM not only to understand natural language but to actively trigger predefined functions in your software.
In this post, we’ll explore what function calling is, why it’s such a significant step forward, and how you can easily integrate it into your own applications using the TTMSMCPCloudAI component from the TMS AI Studio.

What is Function Calling?
At its core, function calling lets an LLM invoke external logic—like APIs or app-specific procedures—based on the user’s intent.
Rather than just generating text, the model can identify when a user request matches a known "tool" or "function," understand its parameters, and return a structured payload that your application can process. Your code then executes the appropriate function and sends the result back to the model, closing the loop between natural language and real-world action.
Imagine asking:
“What’s the weather in Tokyo?”
With function calling, the model recognizes this intent, fills in the required parameter (city: "Tokyo"), and triggers a predefined function like getWeather. Your app runs that function—perhaps calling a weather API—and returns the current forecast.
Why Is This So Powerful?
Function calling allows LLMs to:
-
Perform precise, structured tasks (like querying APIs or databases)
-
Maintain data security by avoiding hallucinations and only accessing defined functions
-
Enable multi-turn workflows, where the model interacts with tools and returns contextual follow-ups
-
Become part of real applications, not just chat interfaces
It bridges the gap between AI as a reasoning engine and AI as a smart assistant executing actual business logic.
Implementing Function Calling with TTMSMCPCloudAI
The TTMSMCPCloudAI component makes it incredibly easy to integrate function calling, abstracting away much of the complexity.
1. Define Tools and Parameters
Each tool represents a callable function. You add tools to the Tools collection of the TTMSMCPCloudAI component and define parameters for each one.
Here’s a minimal example:
This creates a tool called getweather with one required parameter: city. This is a simple example, but tool parameters can be a lot more complex. Multiple parameter's of different types can be added, parameters can be marked as required or not and you can even specify array parameters and define complex types for array elements.
2. Respond to Tool Calls
When the LLM identifies a need to use a tool, the OnExecuteTool event is triggered. You implement this handler to execute your custom logic:
In this example, the LLM supplies the city name, your app calls a weather API, and returns the result—seamlessly integrating AI reasoning with your business logic.
Some more examples
Building further from the GetWeather tool that fetches the current weather conditions and provides it to the AI, now we could add a tool that is able to interact with a map in our Delphi application and put labels on the map. With just this additional tool provided to the LLM, we have an application where the AI can automatically interact with the map and place labels with current weather conditions. The map in this example is our own powerful service-abstract TMS FNC Maps using the Google Maps service.
This is the code to add the tool to TTMSMCPCloudAI that informs the LLM there is a function to add an array of labels on the map at a coordinate Lon,Lat and a string parameter Weather
The code for handling this function call is:
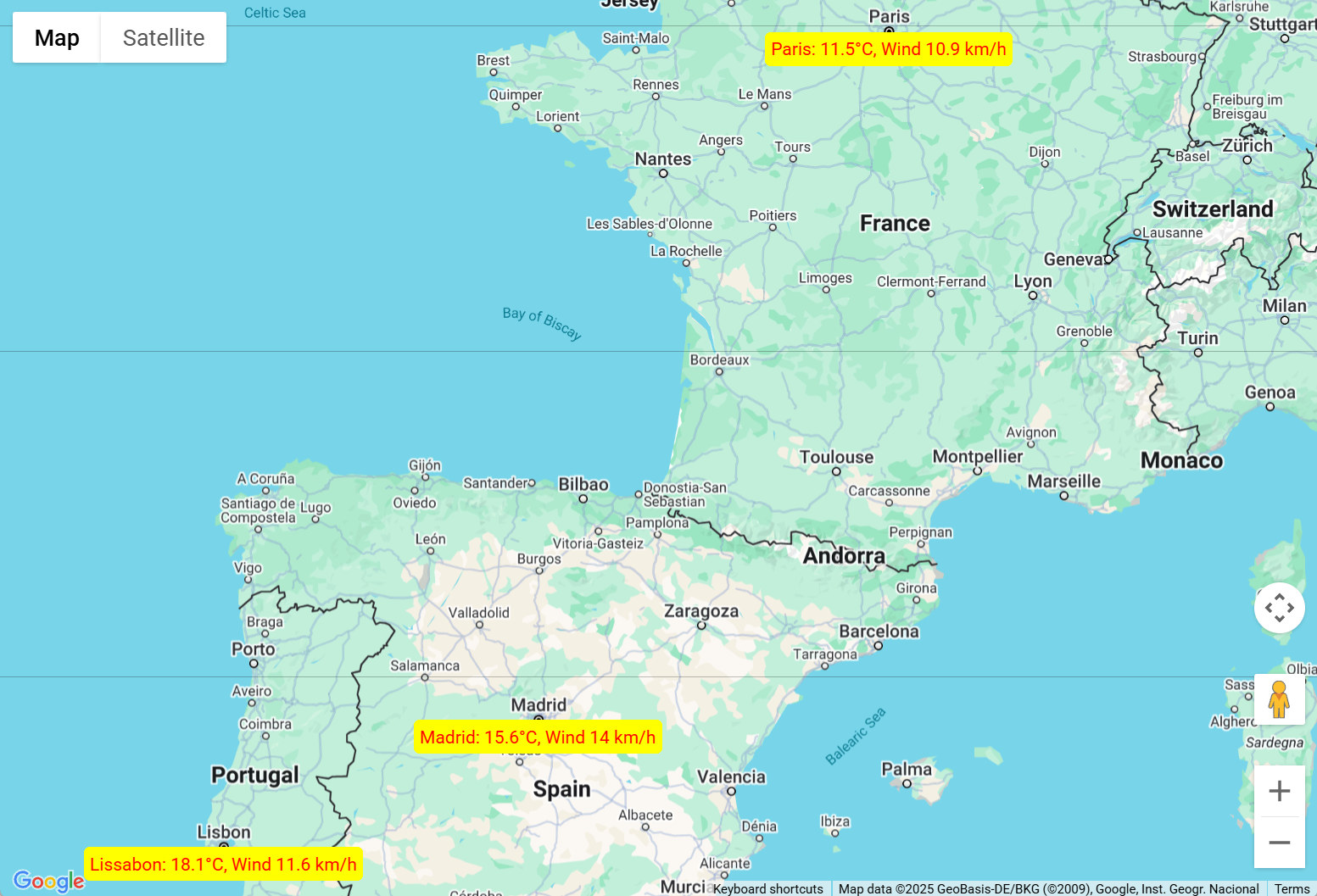
The result for the command below can be seen on the map
"Add a label with the current weather conditions for Paris, Madrid and Lissabon"
Another example is to use the LLM to convert natural language to SQL commands and have these executed via a Delphi TQuery component. To only thing needed here to help the LLM is inform the LLM what fields are in our databse. This can be done by adding a parameter-less tool that will add the fields displayed in a grid (TMS FNC DataGrid in this case) and a tool with one string parameter holding the SQL command to execute the it. Configuring the tools is all done at design-time without adding a single line of code!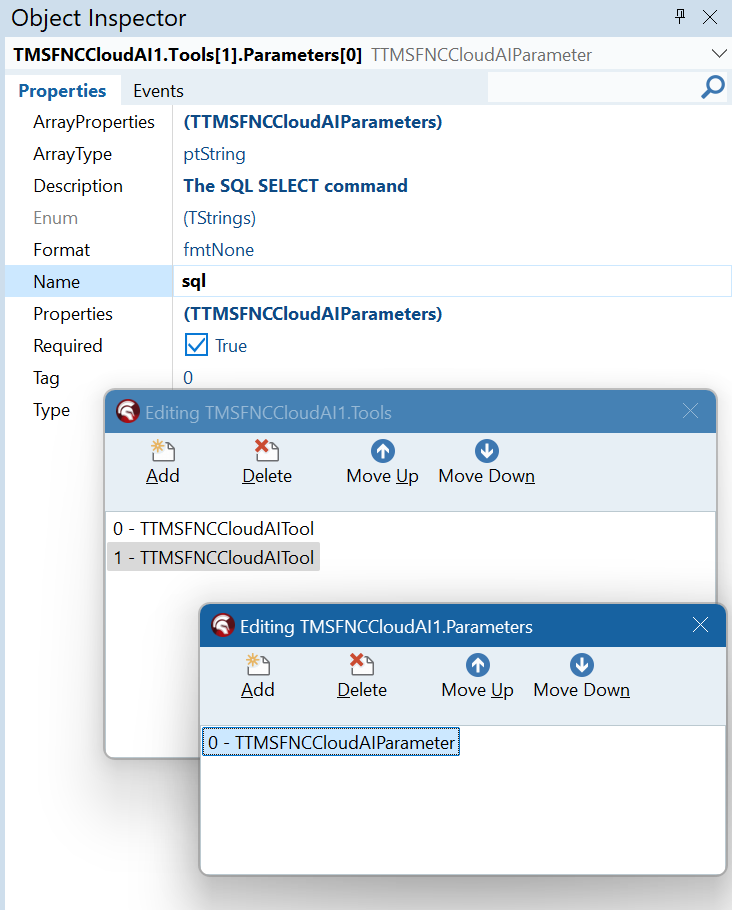
The handlers for these two tools are:
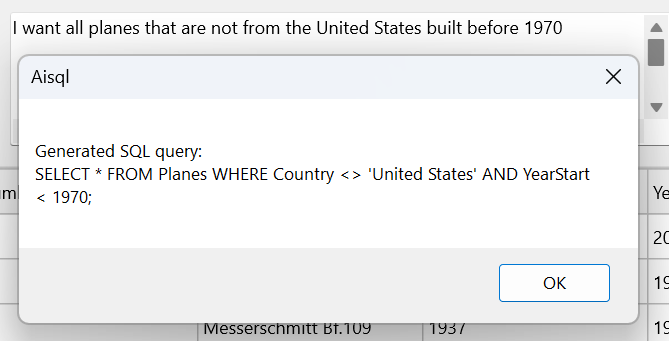
With this tool provided, it is smart enough to convert the natural language to a SQL command and have it executed:
More use cases?
It looks to me that the uses for this are more limited by our imagination than the tecnical details. I can't wait to hear your feedback about other innovative use cases for this technology. Be in touch and we'll be eager to assist you!
Works Across Cloud LLM Providers

This setup works with any supported LLM that includes function/tool calling capabilities—such as OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, Mistral, Ollama, Grok or DeepSeek. TTMSMCPCloudAI abstracts the provider differences and lets you focus on the tool logic! That is the power of TMS AI Studio where you never worry about the nitty gritty details of the REST APIs behind it.
Conclusion
Function calling is a cornerstone of next-generation AI applications. It turns a passive model into an active collaborator—understanding, delegating, and executing tasks. With the TTMSMCPCloudAI component, implementing this is as easy as defining tools, adding parameters, and writing a bit of code in an event handler.
If you’re using LLMs in your application and haven’t yet explored function calling, now’s the time.
In upcoming articles, we’ll dive deeper into image processing AI, RAG, agents, MCP servers & clients.
If you have an active TMS ALL-ACCESS license, you have access to TMS AI Studio that uses the TTMSMCPCloudAI component but also has everything on board to let you build MCP servers and clients. 
Bruno Fierens
Related Blog Posts
-
Add AI superpower to your Delphi & C++Builder apps part 1
-
Add AI superpower to your Delphi & C++Builder apps part 2: function calling
-
Add AI superpower to your Delphi & C++Builder apps part 3: multimodal LLM use
-
Add AI superpower to your Delphi & C++Builder apps part 4: create MCP servers
-
Add AI superpower to your Delphi & C++Builder apps part 5: create your MCP client
-
Add AI superpower to your Delphi & C++Builder apps part 6: RAG
-
Introducing TMS AI Studio: Your Complete AI Development Toolkit for Delphi
-
Automatic invoice data extraction in Delphi apps via AI
-
AI based scheduling in classic Delphi desktop apps
-
Voice-Controlled Maps in Delphi with TMS AI Studio + OpenAI TTS/STT
-
Creating an n8n Workflow to use a Logging MCP Server
-
Supercharging Delphi Apps with TMS AI Studio v1.2 Toolsets: Fine-Grained AI Function Control
-
AI-powered HTML Reports with Embedded Browser Visualization
-
Additional audio transcribing support in TMS AI Studio v1.2.3.0 and more ...
-
Introducing Attributes Support for MCP Servers in Delphi
-
Using AI Services securely in TMS AI Studio
-
Automate StellarDS database operations with AI via MCP
-
TMS AI Studio v1.4 is bringing HTTP.sys to MCP
-
Windows Service Deployment Guide for the HTTP.SYS-Ready MCP Server Built with TMS AI Studio
-
Extending AI Image Capabilities in TMS AI Studio v1.5.0.0
-
Try the Free TMS AI Studio RAG App

This blog post has received 2 comments.

 2. Saturday, June 7, 2025 at 10:28:16 PM
Your question was also answered via direct email. At moment of writing this blog article, Perplexity did not support function calling.
2. Saturday, June 7, 2025 at 10:28:16 PM
Your question was also answered via direct email. At moment of writing this blog article, Perplexity did not support function calling.
Bruno Fierens
All Blog Posts | Next Post | Previous Post
Unfortunately, the CloudAIToolsExecute event is not fired, and in the CloudAIExecuted event of the TTMSFNCCloudAI component I only get a response from the LLM model.
Where am I making a mistake?
* what determines the firing of the CloudAIToolsExecute event?
* is Function Calling supported for all LLM models (I am currently using Perplexity)?
* is it possible to get a full demo of the project for this example (AI SQL)?
This is really great work of yours supporting our Delphi code in the AI world.
I would be grateful for your response and support.
Ziółkowski Jacek